In the world of sorting algorithms, Bubble Sort is a classic algorithm. While it may not be the most efficient way to sort large datasets, it is easy to understand and implement. In this article, we’ll explore how to implement Bubble Sort in Python, and we’ll provide you with a step-by-step visual guide and examples to help you understand how this simple algorithm works. Also, I have provided two implementations of bubble sort with their best and worst time complexity.
What is Bubble Sort?
Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping adjacent elements if they are in the wrong order. You swap them according to the order in which you want to sort the list. It is named bubble sort as in the process of sorting, every element will keep on popping and swapping to each other like bubbles :).
Note:
Although Bubble sort is very easy to understand and implement, it is not the most efficient sorting algorithm for large data sets. The time complexity of Bubble sort is O(n^2) in both the worst and average cases. Merge sort is a suitable and efficient algorithm for large data sets. The time complexity of merge sort is O(n * log n) which is way better than Bubble Sort.
Working of Bubble Sort
Here’s how Bubble Sort works:
- We start by comparing the first two elements of the list. If the first element is greater or smaller than the second element, we swap them. If they are already in the correct order, we leave them as they are.
- We then move on to compare the second and third elements, and so on, until we reach the end of the list.
- At the end of this iteration, the last element will reach its place.
- Once we reach the end of the list, we repeat the process, but this time we only iterate up to the second-last element, because the last element is already in its correct position.
- We keep repeating this process until the entire list is sorted.
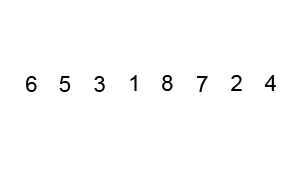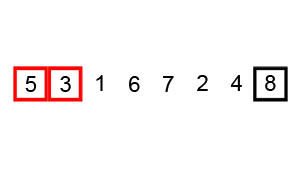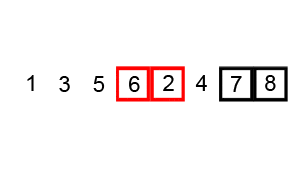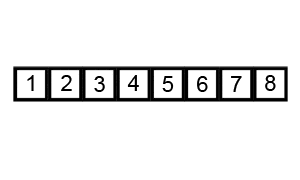
Bubble Sort Algorithm – [Source: Wiki]
Implementation of Bubble sort in Python – Worst
Following is the simplest implementation of Bubble sort where time complexity in all the cases, best and worst, would be O(n^2). Even if the provided array is already sorted, it will still take the same time to return the sorted array. Can we improve it? Refer next implementation
def bubbleSort(arrayToSort):
"""
Time complexity:
best : O(n^2)
average : O(n^2)
worst : O(n^2)
parameters:
arrayToSort : Array to be sorted
returns:
Sorted array
"""
size = len(arrayToSort)
for i in range(size):
for j in range(0, size - i - 1):
if arrayToSort[j] > arrayToSort[j + 1]:
arrayToSort[j], arrayToSort[j + 1] = arrayToSort[j + 1], arrayToSort[j]
print(i, j)
return arrayToSort
Implementation of Bubble sort in Python – Better
In the below implementation, the best time complexity can be O(n). Although the worst or average time complexity in the below implementation would also be the same O(n^2).
def bubbleSort(arrayToSort):
"""
Time complexity:
best : O(n) - when the array is already sorted
average : O(n^2)
worst : O(n^2)
parameters:
arrayToSort : Array to be sorted
returns:
Sorted array
"""
iCount = 0
isSorted = False
size = len(arrayToSort)
while not isSorted:
isSorted = True
for i in range(0, size - iCount - 1):
if arrayToSort[i] > arrayToSort[i + 1]:
arrayToSort[i], arrayToSort[i + 1] = arrayToSort[i + 1], arrayToSort[i]
isSorted = False
print(i)
iCount += 1
return arrayToSort
Interesting Algorithms:
Visit my github repo for all the codes






0 Comments