Hello friends in the last article of VBA Programming Tutorial you have learnt the use of If..else statement. In this lesson you are going to learn another decision making statements in VBA. It means it is another way to control the flow of program, that is nothing but Select… Case structure.
Syntax:
Select Case <test_expression>
Case <condition_1>
<Your code 1>
Case <condition_2>
<Your code 2>
…
Case <condition_n>
<your code n>
Case Else
<your else code>
End Select
Where:
Test Expression: is a string or numeric value which you are going to compare with the list of conditions.
Condition 1, 2…n: These are the different conditions. Whichever condition is going to match with the value of Test Expression, Statements under that condition will be executed. Rest other codes in other conditions will be ignored.
Your Code 1, 2…n: is the code which is going to be execute when the condition is found true.
Note:
Case Else Statement gets executed when none of the conditions are true for a Test Expression. Note that this Statement is an Optional Statement. It means it is not necessary to put Case Else Statement unless you want to execute a piece of code to be executed even when none of the conditions are matching.
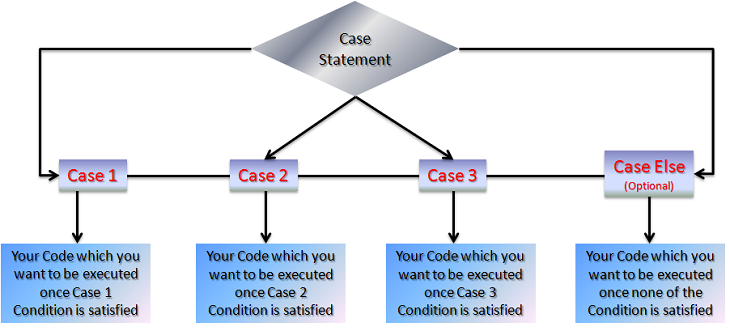
Select Case Statement
Use of Case Statement
It is always a good practice to use Select Case Statement when multiple If-Else conditions are involved. As the number of If-Else conditions increases, debugging and understanding all the flow becomes tedious job. To overcome that problem, It is advised to use Select Case statement in nested If-Else conditions.
Example:
I am going to explain different ways of putting the condition expressions in Case Clause. Refer the below 4 examples:
To Practice your own, you can download this Excel Workbook with all the four examples.
1. Single Expression or value as a Case Condition
In the below example user will be asked to Enter a Number of the Day like 1, 2, 3…7 and using Select Case statement function will return the corresponding Name of the Day. Note: Here first day of the week is considered as “Monday”.
Sub Find_Day_1()
Dim DayNumber As Integer
DayNumber = InputBox("Enter the Day Number")
Select Case DayNumber
Case 1
MsgBox ("Monday")
Case 2
MsgBox ("Tuesday")
Case 3
MsgBox ("Wednesday")
Case 4
MsgBox ("Thursday")
Case 5
MsgBox ("Friday")
Case 6
MsgBox ("Saturday")
Case 7
MsgBox ("Sunday")
Case Else
MsgBox ("Invalid Day Number")
End Select
End Sub
2. Using a comma to separate multiple expressions or ranges in each Case Clause.
Multiple expressions or ranges can be specified in each Case clause, by separating each expression with a comma It is same as logical operator OR. In the below example in each of the Case clause there are two expression: One is numeric and other one is string. It means if you Input : 1 then Also it will return “Monday” and If you enter “Mon” then also it will return “Monday”.
Sub Find_Day_2()
Dim DayNumber As Variant
DayNumber = InputBox("Enter the Day Number")
Select Case DayNumber
Case 1, "Mon"
MsgBox ("Monday")
Case 2, "Tue"
MsgBox ("Tuesday")
Case 3, "Wed"
MsgBox ("Wednesday")
Case 4, "Thurs"
MsgBox ("Thursday")
Case 5, "Fri"
MsgBox ("Friday")
Case 6, "Sat"
MsgBox ("Saturday")
Case 7, "Sun"
MsgBox ("Sunday")
Case Else
MsgBox ("Invalid Day Number")
End Select
End Sub
3. Using To Keyword to Specify upper and lower limit of a range.
If you want to compare a value within a range then you can use To Keyword in your case clause as shown in the below example. Below example will take Marks in Percentage as input and it will return the Grade of the Student based on which range does that % belongs to.
Sub Find_Grade()
Dim Percentage As Integer
Percentage = InputBox("Enter the Obtained Percentage Marks by a Student")
Select Case Percentage
Case 0 To 33
MsgBox ("Failed")
Case 33 To 44
MsgBox ("Third Div")
Case 45 To 59
MsgBox ("Second Div")
Case 60 To 74
MsgBox ("First Div")
Case 75 To 100
MsgBox ("First Div with Distinction")
Case Else
MsgBox ("Marks Obtained in % Can not be more than 100")
End Select
End Sub
4. Using the Is Keyword with a comparison operator to compare.
Using Is keyword you can compare the case value using comparison operator like < , > ,=<, >= etc. as shown in the below example:
Sub Find_Temp_Status()
Dim temp As Single
temp = InputBox("Enter the Temperature")
Select Case temp
Case Is >= 40
MsgBox "Extremely Hot"
Case Is >= 25
MsgBox "Moderately Hot"
Case Is >= 0
MsgBox "Cool Weather"
Case Is < 0
MsgBox "Extremely Cold"
End Select
End Sub




Hi Vishwa,
This is very nice and informative. I like the detailed examples you have given for the article on CASE statement.
Thanks,
Venkat.
Thanks Venkat !!