Dear Friends,
Here in this article, I have tried to consolidate some most useful and more frequently used excel macro with examples. This is part 1 where I have provided 20 Excel Macros related to workbooks and worksheets. Remaining 20 Excel Macro examples will be followed in my next article – 40 Useful Excel Macro examples for Beginners – Part 2 of 2
Note: These are very simple yet useful and most used functions/statements in Excel VBA. To use them, make sure that you change the Excel file path, name, sheet name, etc. change it to fit your workbook, and then run it. They should do the job which they are written for.
Download a FREE Excel Workbook with all 40 Examples
At the end of the second part of this tutorial, I will publish a link to download all 40 Excel Macros collection Workbooks for FREE.
If you have any questions or feedback, write them in the comment below.
Workbook Related:
1. Create a New Excel Workbook using Excel Macro
2. Open an existing Excel Workbook using Excel Macro
3. Close a workbook without saving the changes using Excel Macro
4. Close a workbook by saving the changes using Excel Macro
5. Save or SaveAs a workbook using Excel Macro
6. Delete a workbook using Excel Macro
WorkSheets related:
7. Add a new worksheet in a workbook using Excel Macro
8. Add a worksheet at a specified position using Excel Macro
9. Rename a worksheet using Excel Macro
10. Delete a worksheet using Excel Macro
11. Change the tab colour of a worksheet using Excel Macro
12. Copy a worksheet within same workbook using Excel Macro
13. Copy a worksheet as a new Workbook using Excel Macro
14. Copy a worksheet by providing sheet name of your choice using Excel Macro
15. Hide a worksheet using Excel Macro
16. Hide all worksheets except activeSheet using Excel Macro
17. Unhide a worksheet using Excel Macro
18. Unhide all worksheets in a workbook using Excel Macro
19. Check if a sheet with particular name exists in a workbook using Excel Macro
20. Sort all worksheet alphabetically using Excel Macro
Excel Macro to Create a new Excel workbook file
Use the following Excel VBA code to create a new Excel Workbook and save it as a given path as shown in the below code.
Sub CreateNewExcelWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Add
' now if you want to save this new workbook
' save it by providing the full name of the file
wb.SaveAs "C:\abc\temp.xlsx"
End Sub
Excel Macro to open an existing excel workbook
Refer the following Excel VBA code to open an existing excel workbook which is saved at a given path.
To run the below code, do not forget to change the file path which I have provided.
Sub openExcelWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\....\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
'given workbook is opened and it is referred by
' the variable wb of type workbook
' now you can do all the operations on wb which
' you want to do on this workbook
'For Example to close this workbook
wb.Close
End Sub
Note: Once you opened your workbook, you should set it to a variable of Workbook type, so that you can refer this workbook by this variable wherever you want to use in your program.
Excel Macro to close a workbook with or without saving the changes
It is logical that after working on your workbook, at the end of the progrma you want to keep closing the workbook which you VBA program is using. So here is the example of closing your workbook.
As you know on closing an opened workbook, there are two possibilities:
1. Close the workbook without saving all the changes which are not saved yet
2. Close the workbook without saving any of the unsaved changes
It is very simple to do using Excel VBA. While closing if set the SaveChanges parameter to true then changes will be saved and if it is set to false then changes will be ignored. Refer the below code…
Sub closeWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\....\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' For Example:
' To close this workbook with
' saving the changes
wb.Close SaveChanges:=True
' To close this workbook without
' saving the changes
wb.Close SaveChanges:=False
End Sub
Excel Macro to save or saveAs a workbook
As you must be aware of the difference between Save and SaveAs. It is same here in Excel vba as well.
If you want to save the changes in the same file then you can use the Save statement in Excel VBA else SaveAS.
Note: For saveAs you need to provide the complete path[including file name] for the new file where you want to save it.
Sub saveWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim fPath As String
Dim newPath As String
fPath = "C:\....\myfile.xlsx" ' old path
newPath = "D:\....\myfile1.xlsx" ' new path
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' To save your workbook at the same
' location with same name
wb.Save
' to save your workbook on a different location
' or with a different name or both
wb.SaveAs Filename:=newPath
End Sub
Excel Macro to delete a workbook
You can use the following example to delete a workbook.
Note: Kill statement is basically used to delete any file using Exel VBA. So you can even delete some word doc, text file etc.
Sub deleteFile()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim fPath As String
' full path of the file which you want to delete
' this is not necessarily to be excel file
' it can be any file
fPath = "C:\....\myfile.xlsx"
' this statement will delete the file
Kill PathName:=fPath
End Sub
Excel Macro to add a new worksheet in a workbook
So far in the above examples, you had seen how to deal with Workbook itself like opening, closing, saving, deleting etc.
Now using the below example you can add a new WorkSheet in a Workbook. To perform any such operations on a workbook, you first need to have a Workbook, therefore you will see that in all the below examples, I have first opened a workbook and assigned that Workbook to a variable wb.
Sub addNewSheetInAWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\....\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' Add a new worksheet in your workbook
wb.Worksheets.Add
End Sub
Note: In the above statement after .add there is no other parameter specified therefore new sheet will be added before the activesheet.
Excel Macro to add a worksheet at a specified position
As mentioned in the above example, if do not provide the position parameter while adding a new sheet in a workbook, by default it will get added before the activeSheet.
Now here in the below example, I am showing you – how can you provide the position parameter while adding a new sheet.
Refer the comments… written inside the code.
Sub addNewSheetInAWorkbookAtPosition()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\....\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' Add a new worksheet in your workbook
' Below statement will add your new sheet at first position
wb.Worksheets.Add Before:=1
' Below statement will add your new sheet at second position
wb.Worksheets.Add After:=1
' Below statement will add your new sheet at the end
wb.Worksheets.Add After:=Worksheets.Count
End Sub
Excel Macro to rename a worksheet
Renaming is simply done by setting new name of the worksheet to the .Name property of a worksheet as shown in below code
Sub renameWorksheet()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim newSheetName As String
newSheetName = "March"
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' Rename the sheet name of the 1st sheet
Set sh = wb.Worksheets(1)
sh.Name = newSheetName
End Sub
Excel Macro to delete a worksheet
.Delete method of WorkSheet Object can be used to delete a worksheet.
Sub deleteWorksheet()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim newSheetName As String
newSheetName = "March"
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' delete first worksheet
Set sh = wb.Worksheets(1)
' Following statemet will launch an excel built in
' delete confirmation popup message.
' once you confirm it manually then this sheet would be deleted
sh.Delete
End Sub
As mentioned in the above code’s comment section, it would display a delete confirmation popup message for your to confirm the deletion manually. Once you confirm, then deletion will take place.
You can easily get rid of this popup by setting the following…
Application.DisplayAlerts = False ' to disable to delete confirmation popup
sh.Delete ' now delete the sheet
Application.DisplayAlerts = True ' to disable to delete confirmation popup
Note: If you do not enable the Application.DisplayAlert flag after deleting your sheet then you would not even get this delete confirmation popup when you try to delete a sheet manually.
To know more about this, you can read my detailed article here…
Excel Macro to change the tab color of a worksheet
Tab color of sheets in a workbook can be changed by .Tab.ColorIndex or .Tab.Color
ColorIndex always accept a number for the color while .Color accepts RGB format of any color. You can refer these two in the below code.
Sub ChangeTabColor()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim newSheetName As String
newSheetName = "March"
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' delete first worksheet
Set sh = wb.Worksheets(1)
' refer the color indexes and actual colors
' in the below image
sh.Tab.ColorIndex = 1
' you can also use RGB format for defining the color code
sh.Tab.Color = RGB(255, 0, 300)
End Sub
Excel Macro to copy a worksheet within same workbook
Read the comments in the below code. Using this example, you can copy an existing worksheet in a workbook at any given postition like at the beginnig, end or second etc. positions.
Refer the below example:
Sub CopySheet()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim newSheetName As String
newSheetName = "March"
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' make a copy the first sheet
Set sh = wb.Worksheets(1)
' Copy the worksheet at first position
sh.Copy Before:=Sheets(1)
' Copy the worksheet at last position
sh.Copy After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count)
End Sub
Excel Macro to copy a worksheet as a new Workbook
As you might have seen in Excel Workbook that it is possible to Copy a worksheet as a New Workbook manually.
This is same thing done by using Excel Macro.
Note: If you pass a position parameter in .Copy method then Worksheet will be copied within the same workbook[like in the above example] but if you skip the position parameter [like in below example] then it will be copied as a new Workbook.
Sub CopySheet()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim newSheetName As String
newSheetName = "March"
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' make a copy the first sheet
Set sh = wb.Worksheets(1)
' Copy the worksheet as a new workbook
sh.Copy
End Sub
Note: If you do not use the parameters like Before or After, then .Copy will copy your worksheet as a newWorkbook with only your worksheet.
If you want to copy more than one sheets to a new workbook then you can use Array to copy as shown below
Excel Macro to copy multiple worksheets as a new Workbook
Sub CopySheetAsWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim newSheetName As String
newSheetName = "March"
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' this will copy all 3 sheets to a new workbook
wb.Worksheets(Array("Sheet1", "Sheet2", "Sheet3")).Copy
End Sub
Excel Macro to copy a worksheet by providing sheet name of your choice
Sub CopySheetWithProvidedName()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim newSheetName As String
newSheetName = "March"
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
' make a copy the first sheet
Set sh = wb.Worksheets(1)
' Copy the worksheet as a new workbook
sh.Copy Before:=Sheets(1)
ActiveSheet.Name = "your own name3"
End Sub
Note: After making a copy of any sheet… copied sheet becomes activesheet. Therefore all you need to do is provide your own name to the activesheet.
Excel Macro to hide a worksheet
Using .Visible property you can hide or unhide a worksheet.
Sub HideWorksheet()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim newSheetName As String
newSheetName = "March"
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
'
Set sh = wb.Worksheets(1)
' Hide the first worksheet
sh.Visible = xlSheetHidden
End Sub
Excel Macro to unhide a worksheet
Using .Visible property you can hide or unhide a worksheet.
Sub HideWorksheet()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim newSheetName As String
newSheetName = "March"
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
'
Set sh = wb.Worksheets(1)
' unhide the first worksheet
sh.Visible = xlSheetVisible
End Sub
Excel Macro to hide all worksheets except activeSheet
Sub HideAllWorksheets()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
For Each Sheet In wb.Worksheets
If Sheet.Name <> ActiveSheet.Name Then
Sheet.Visible = False
End If
Next
End Sub
Excel Macro to unhide all worksheets in a workbook
Sub UnhideAllWorksheets()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim fPath As String
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
For Each Sheet In wb.Worksheets
If Sheet.Name <> ActiveSheet.Name Then
Sheet.Visible = True
End If
Next
End Sub
Excel Macro to check if a sheet with particular name exists in a workbook
Sub CheckIfSheetExists()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim fPath As String
Dim sheetExists As Boolean
sheetExists = False
fPath = "C:\Users\vmishra\Desktop\myfile.xlsx"
Set wb = workbooks.Open(Filename:=fPath)
For Each Sheet In wb.Worksheets
If Sheet.Name = "SheetName To Search" Then
sheetExists = True
Exit For
End If
Next
If sheetExists Then
MsgBox "Yes, SheetName To Search exists in the workbook"
End If
End Sub
Excel Macro to sort all worksheet alphabetically
If you want to sort all the worksheets in your workbook in alphabetical order, then copy paste following code in any module and run it.
Sub SortSheetNames()
' Sort all the sheets alphabetically
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
Dim totalSheets As Integer
totalSheets = Sheets.Count
For i = 1 To totalSheets - 1
For j = i + 1 To totalSheets
If Sheets(j).Name < Sheets(i).Name Then
Sheets(j).Move Before:=Sheets(i)
End If
Next j
Next i
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub




Very very useful article … if possible please provide with downloadable excel workbook
Thanks Pravesh for feedback… This Friday on 29th, second part of this tutorial with remaining 20 useful macros will be published. Then i can provide a download link of Excel with all 40 Macros with Examples.
You are Super Vishwamitra Ji,
Great Job….
Waiting for your tutorial…
Advice me for my carrier with Data Analysis
B.Com, MBA in Operation
Working with Advance Excel like(Power Pivot Table,Power Query)
Microsoft Power BI(Basic report like MOM,YOY)
MS Access (Basic Report)
Thanks Pramod !! Next tutorial is going to be published soon before this weekend [mostly on this friday]
Thanks for this!
You are welcome !!
I downloaded the excel workbook and when I opened it there was nothing there. Am I the only one having this issue?
Dear Stacey,
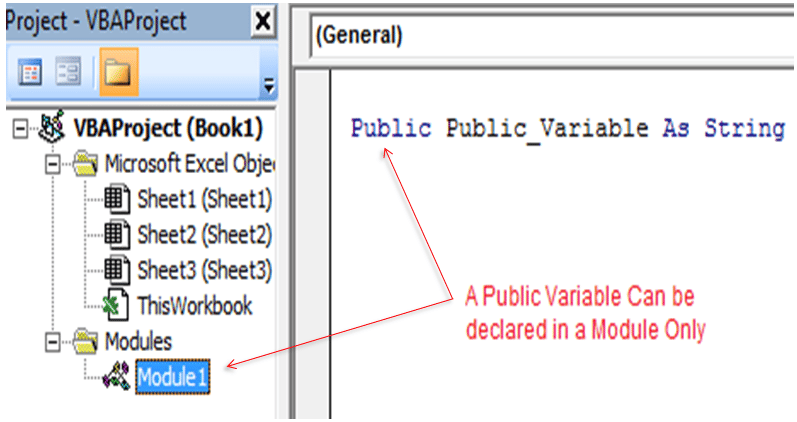
Once you have opened the workbook, pres Alt+ F11
There you will see two modules in the VBA Project – part1 and part2.
They both have all the excel macros [20 each
Let me know if this helps !!
Thank you so much.
From thailand
interesting ! Thanks for information !
thanks for your good data
Hi will you able to help me with the macro
a) To Delete all the sheets except present work book
b) I like to send individual email, based on the key words eg Customer Name( the base records will have multiple records for same key words eg Sales Register which has same customer billed multiple times)
Tks
great
thanks for good data
great thanks for yourgood data
Thanks for information!