The most easiest and commonly used function in VBA is Input Box. Without much VBA coding, user can be asked to enter some input at any point of programming. To illustrate the simplicity of Input Box we will take an example.
Example: You are trying to add a New WorkSheet in a Workbook but the Sheet Name you want to be provided by the user run time. When I say “Run Time” It means after running the program you are asked for the Name of the sheet and once you enter it a new sheet is created with the same name you entered. You can read more on Adding sheet using VBA in this article
Sub Add_Sheet()
Sheets.Add.Name = InputBox(Title:="Title Name", _
Prompt:="Prompt Name", _
Default:="Default Value", _
xPos:=100, yPos:=100, _
HelpFile:="Demo.help", _
Context:=2)
End Sub
Above Code will add a New sheet in the Excel workbook, with the same name which entered in to the Input Box appeared.
Note: This is a very simple code to add a sheet. It does not have any validation like checking if any sheet with the same name exist or not. To handle all such validation you can read this article.Click Here
Syntax:
InputBox(prompt[, title] [, default] [, xpos] [, ypos] [, helpfile, context])
Prompt(Required): This is the message which you want to be displayed in the dialog box (Input Dialog Box). For example: “Enter your Sheet Name”
Title (Optional): This is the Title which you want to be displayed in the title bar of the dialog box. If you do not provide title, then application name is displayed in the title bar by default.
Default (Optional): This is value which you want to be displayed by default as soon as InputBox is launched. If you do not pass this parameter then it will remain blank by default.
xPos Optional. Numeric value which displays the distance of the dialog box from Left side of the Screen. By default it is centrally aligned to the screen.
yPos (Optional): Numeric value which displays the distance of the dialog box from upper side of the Screen. By default it is vertically positioned approximately one-third of the way down the screen.
HelpFile (Optional): If you want Help button to be displayed on the InputBox then you can pass HelpFile Name in this parameter.
Context (Optional): Numeric expression that is the Help context number assigned to the appropriate Help topic by the Help author. If context is provided, helpfile must also be provided.
On Running the above code, InputBox will appear like this:
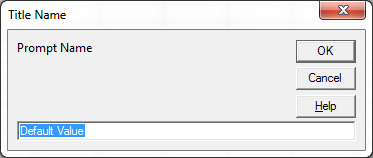
VBA : Input Box
Let’s take another example where you want user to enter a valid Cell Range to perform some operation on that range.
Sub ClearSelectedArea()
Dim rng As Range
Dim strAddress As String
strAddress = InputBox("Select the cells to be cleared")
Set rng = Range(strAddress)
rng.Select
Selection.ClearContents
End Sub
When InputBox dialog Box opens then your Excel Workbook get frozen. It means you can not select any cell or do anything until you closes the InputBox dialog box. It means this kind of InputBox is good for users to enter any text or number. But in the above example if you see, It is difficult to Input a range Address in input box without having flexibility to see and select the cells or cell-range. Without doing so you will not be able to select.
This is where the other InputBox comes in to picture. Technically the InputBox which we have used before is called as “VBA InputBox Function” and the other InputBox (which I am calling it as Smart InputBox) is an InputBox method in Excel VBA.
Since this Smart InputBox is a method in Excel VBA, therefore, it must be used like this:
rng = Application.InputBox(“Select the Cells to be cleared”)
From the above code, it looks very much similar to what we have used in normal InputBox but there are few differences in the functionality.
As I told smart InputBox is a VBA method, it means It is not necessary that it will return only string. It may return different types of values like Boolean type, Range Object or a number. This InputBox method can return different types of values, then there must be an identifier which tells user which type of value it should return.
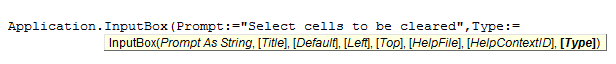
InputBox Method
In the above picture the Type parameter is to determine the type of the return value. For different types of values, there are different types which you need to mention.
For example, in above case when you want that a user has to select a range address then you need to pass the Type Parameter as 8.
Below table shows the different Type Values and corresponding data types:
| Type Value | Type Meaning |
| 0 | A formula |
| 1 | A number |
| 2 | Text (a string) |
| 4 | A logical value (True or False) |
| 8 | A cell reference, as a Range object |
| 16 | An error value, such as #N/A |
| 64 | An array of values |
Therefore in the above example we can use the InputBox method to take the range object from the user and we need to pass the type parameter as 8.
Sub ClearSelectedArea() Dim rng As Range Dim strAddress As String strAddress = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Select the cells to be cleared",Type:=8) Set rng = Range(strAddress) rng.Select Selection.ClearContents End Sub
InputBox Method looks little different from the InputBox function as show below:
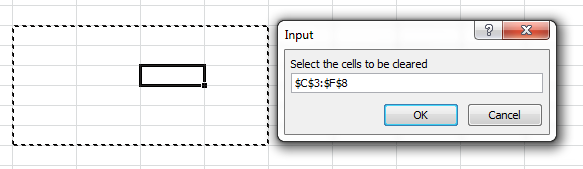
InputBox-Method
Now in the above example you can see that InputBox is accepting only valid excel range. Even if you try to enter an invalid Range Input then it will throw an error. This is the reason I prefer calling it as Smart InputBox because it does the validation before accepting any value entered by the user.




Nice Article.. I really liked your presentation and explanation about the input box. Indeed it is a smart inputbox.
Thanks Harsh !!
Thanks Harsh for your words 🙂